Video Article Open Access
Is Micromachined Topography of Polydimethyl-Siloxane Surface Effective for Observation of Biological Cell Behavior?
Shigehiro Hashimoto
Kogakuin University, Tokyo, 1920015, Japan
Vid. Proc. Adv. Mater., Volume 2, Article ID 2021-0164 (2021)
DOI: 10.5185/vpoam.2021.0164
Publication Date (Web): 09 Feb 2021
Copyright © IAAM
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
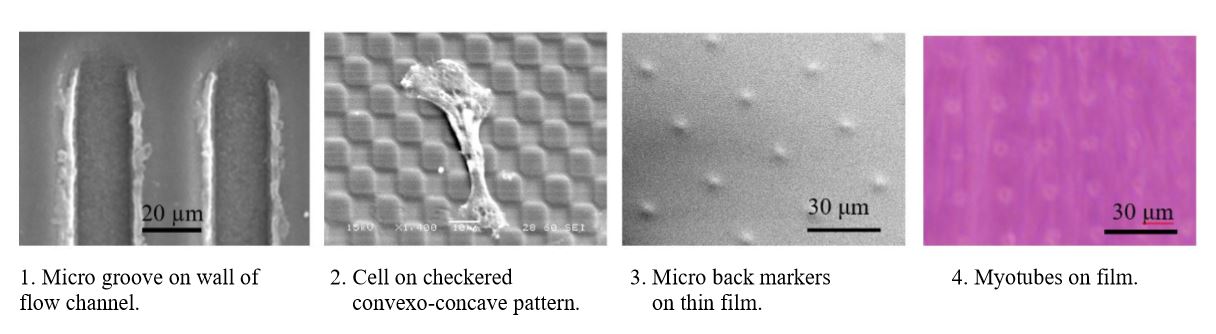
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is the typical base material for micromachining by photolithography. Biological cells adsorb on the scaffold, and show activities: migration, deformation, proliferation, and differentiation. The micro topography (close to the cell size) on the surface of the scaffold is effective for several applications: the marker to trace each cell, and the tool to control the activity of each cell. C2C12 (mouse myoblast) is used in the present study. The typical diameter of the cell is 20 μm, when it is suspended in the medium. The cell aligns along the micro step of the height (> 0.7 μm). The micro-striped groove can control the cell migration direction in the flow channel. The aspect ratio of the checkered convexo-concave pattern can control the orientation of cells. When cells are cultured on the thin film (thickness 6 μm) of PDMS with micro markers at the counter surface, local contraction movement of myotubes by electrical-pulse stimulation can be microscopically measured through the transparent scaffold. Deformability of each cell can be detected by the flow through the micro slit of PDMS.
Keywords
Surface topography; photolithography; polydimethylsiloxane; orientation.
Acknowledgement
The experimental work was supported by Dr. Haruka Hino, Dr. Yusuke Takahashi, Mr. Fumihiko Sato, Mr. Yusuke Shinozaki, Mr. Hiromi Sugimoto, Mr. Kenta Sugimoto, and Mr. Daisuke Watanabe.
References
- H. Hino, S. Hashimoto, Y. Shinozaki, H. Sugimoto, Y. Takahashi, Journal of Systemics Cybernetics and Informatics, 2017, 15(5), 1.
- S. Hashimoto, K. Sugimoto, Y. Takahashi, Proc. 22nd World Multi-Conference on Systemics Cybernetics and Informatics, 2018, 2, 13.
- Y. Takahashi, S. Hashimoto, K. Sugimoto, D. Watanabe, H. Hino, Journal of Systemics Cybernetics and Informatics, 2017, 15(4), 1.
- S. Hashimoto, Advanced Materials Letters, 2020, 11(3), 1.
- P. N. Carlsen, Polydimethylsiloxane: Structure and Applications, Nova Science Publishers, 2020, 29.
Biography
Shigehiro Hashimoto is Professor of Biomedical Engineering (2011-), and Dean (2018-), Faculty of Engineering of Kogakuin University, Tokyo, Japan. Bachelor of Engineering in Mechanical Physics (1979), Master (1981), and Doctor of Engineering (1990) at Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo, Doctor of Medicine at Kitasato University (1987), Sagamihara. Research Associate in School of Medicine (1981-1989), and Assistant Professor in School of Medicine (1989 -1994), at Kitasato University, Associate Professor in the Department of Electronics (1994-2001), and Professor (2001-2011) at Osaka Institute of Technology. Creator of the first Department of Biomedical Engineering in Japan at Osaka Institute of Technology (2005) and Director of its Medical Engineering Research Center (2005-2011). Associate to President and Dean of Admissions Center at Kogakuin University, Tokyo (2012-2018). Internship in Research Center for Artificial Heart in Free University in Berlin (1977). Author of the books of “Introduction to Biosystems Engineering (1996)”, “Introduction to Biomedical Measurement Engineering (2000)”, and “Introduction to Biomechanical Engineering (2013)”. Researches are focused on bio-cellular mechanics study using micro-machined flow channel.
Video Proceedings of Advanced Materials

Upcoming Congress



